Most enterprises rush to implement agentic AI systems, focusing on model selection and prompt engineering. Then they hit a wall: their infrastructure can’t handle autonomous agents making decisions, executing code, and orchestrating workflows. The bottleneck isn’t the AI—it’s the architecture.
This guide covers what actually matters when deploying agentic AI in production: the infrastructure, security, and operational patterns that separate successful deployments from failed pilots.
This isn’t about model capabilities. GPT-4, Claude, and Gemini are impressive. The problem is infrastructure: siloed data, inadequate access controls, missing orchestration layers, and governance gaps. In healthcare, where I work, HIPAA compliance adds another layer of complexity that many AI vendors ignore.
In this comprehensive analysis, I’ll share what I’ve learned from enterprise AI deployments, the infrastructure gaps that kill projects, and a practical roadmap for readiness. This is the guidance CTOs and enterprise architects need—honest, actionable, and based on real deployments.
What You’ll Learn
- The infrastructure readiness gap and why it matters
- Why technical capability ≠ enterprise readiness
- Real barriers: siloed data, access controls, observability
- Assessment framework: Is your organization ready?
- 6-12 month roadmap for infrastructure enablement
- Healthcare-specific considerations (HIPAA, audit trails)
- System integration with legacy ERP/CRM systems
- Data quality and governance prerequisites
- Orchestration layers, monitoring, and escalation paths
- Real-world case studies and lessons learned
The Infrastructure Readiness Gap: What Gartner’s Prediction Really Means
Gartner’s prediction that 40% of agentic AI projects will be cancelled by 2027 isn’t about AI capability—it’s about infrastructure readiness. According to their June 2025 report, the primary reasons for cancellation are:
- Escalating costs: 35% of projects exceed budget due to infrastructure complexity
- Unclear business value: 28% fail to demonstrate ROI because integration is incomplete
- Inadequate risk controls: 37% are cancelled due to governance and compliance gaps
These aren’t AI problems. They’re infrastructure problems. The models work. The integrations don’t.
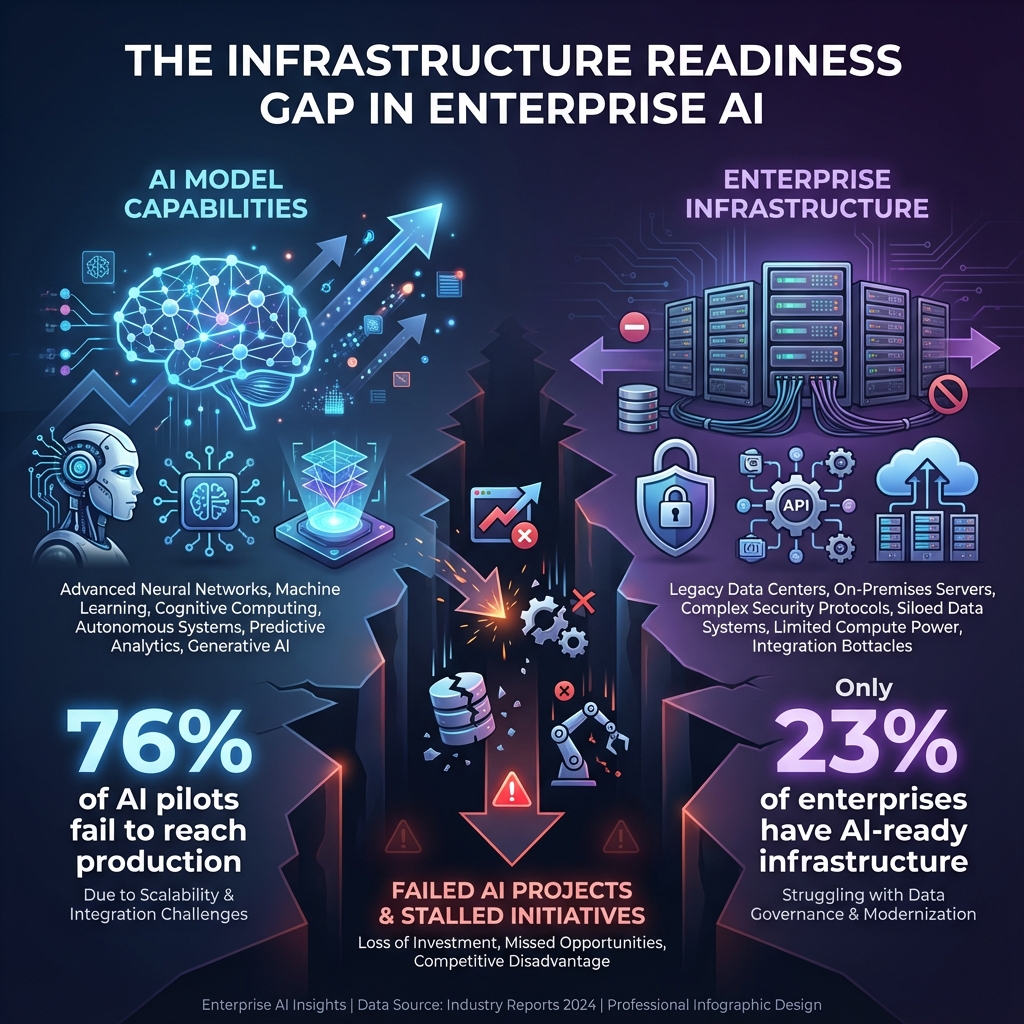
Figure 1: Infrastructure Readiness Gap
1. Why Technical Capability ≠ Enterprise Readiness
Vendors sell AI capability. Enterprises need integration, governance, and reliability. These are different problems.
1.1 The Capability Trap
Modern LLMs are impressive. GPT-4, Claude 3.5, and Gemini Pro can reason, code, and analyze. But enterprise deployment requires more than model capability:
- Integration: Connecting to legacy ERP, CRM, and EMR systems
- Governance: Access controls, audit trails, compliance
- Reliability: Error handling, fallbacks, monitoring
- Scalability: Handling enterprise-scale workloads
- Security: Data protection, encryption, access management
I’ve seen teams deploy GPT-4 successfully in a lab, then fail in production because they couldn’t integrate with their Epic EMR system or maintain HIPAA-compliant audit trails.
1.2 The Integration Challenge
Legacy systems weren’t designed for AI. They have:
- Proprietary APIs: Custom protocols, not REST/GraphQL
- Data silos: Information scattered across systems
- Access controls: Complex permission models
- Compliance requirements: HIPAA, SOX, GDPR
AI agents need to navigate these systems, but most AI frameworks assume modern APIs and clean data.
2. Real Barriers: The Infrastructure Gaps
2.1 Siloed Data: The Integration Nightmare
Enterprise data lives in silos. Patient data in Epic, claims in Mainframe, provider data in Salesforce. AI agents need unified access, but integration is complex.
The Problem:
- Data fragmentation: Information scattered across 10+ systems
- Inconsistent formats: HL7, EDI, proprietary formats
- Access complexity: Different authentication for each system
- Real-time vs batch: Some systems only support batch updates
Real Example: At Evernorth, we needed an AI agent to check patient eligibility. The data was in three systems: Epic (clinical), Mainframe (claims), and Salesforce (provider network). Each had different APIs, authentication, and data formats. Building the integration layer took 6 months—longer than building the AI agent itself.
# Example: Integrating with legacy systems
class LegacySystemAdapter:
"""Adapter pattern for legacy system integration"""
def __init__(self, system_type):
self.system_type = system_type
self.connector = self._get_connector()
def _get_connector(self):
if self.system_type == "epic":
return EpicHL7Connector()
elif self.system_type == "mainframe":
return Mainframe3270Connector()
elif self.system_type == "salesforce":
return SalesforceRESTConnector()
def get_patient_data(self, patient_id):
"""Unified interface for patient data"""
# Transform to common format
raw_data = self.connector.fetch(patient_id)
return self._normalize(raw_data)
def _normalize(self, data):
"""Normalize data from different systems"""
# Handle different formats, schemas, etc.
pass
2.2 Inadequate Access Controls
Enterprise access control is complex. AI agents need permissions, but granting too much creates risk.
The Challenge:
- Role-based access: Different permissions for different roles
- Data sensitivity: PHI, PII require special handling
- Audit requirements: Every access must be logged
- Dynamic permissions: Access can change based on context
Most AI frameworks assume simple API keys. Enterprise needs fine-grained, auditable access control.
2.3 Poor Observability
When an AI agent makes a decision, you need to know:
- What it did: Actions taken, systems accessed
- Why it did it: Reasoning chain, data used
- What went wrong: Errors, failures, edge cases
- Who was affected: Patients, members, providers
Traditional monitoring doesn’t capture AI agent behavior. You need specialized observability for agentic systems.
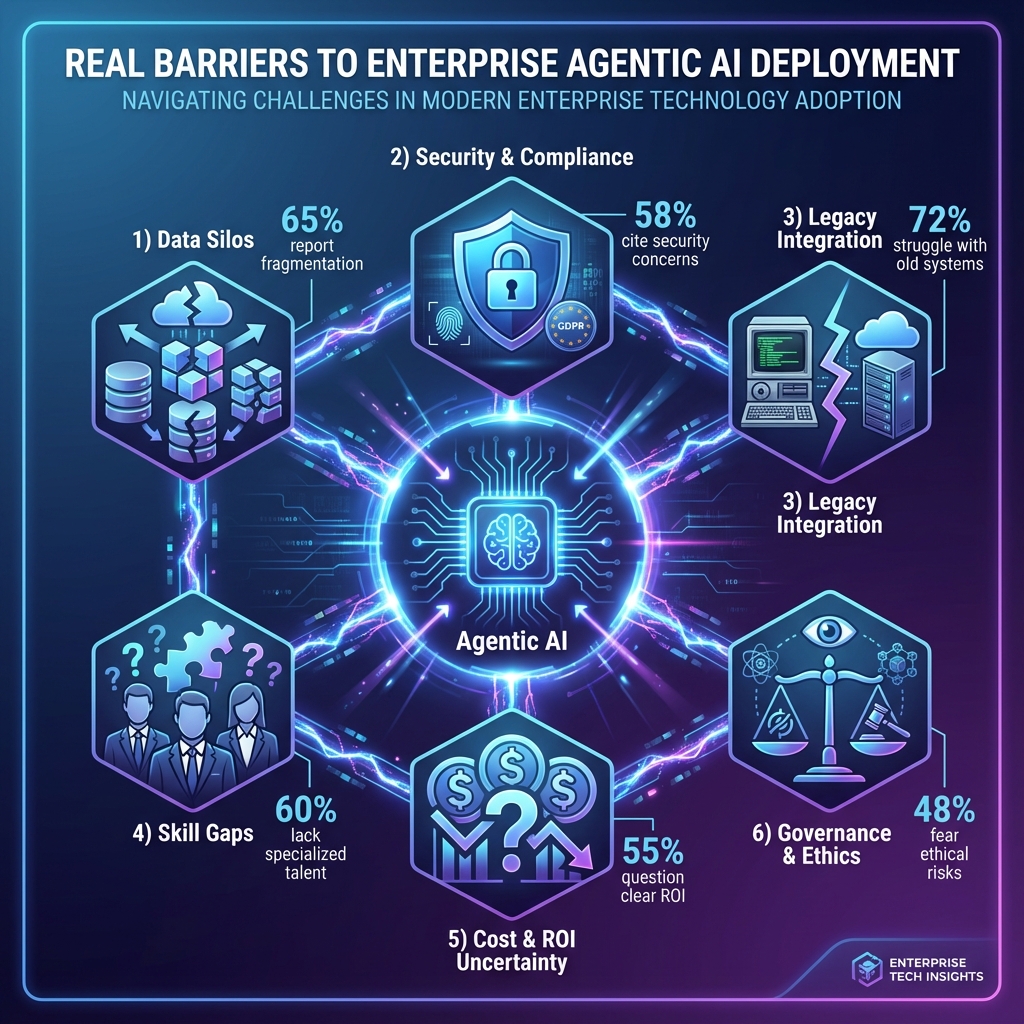
Figure 2: Real Barriers to Enterprise AI
3. System Integration Complexity
3.1 Legacy ERP/CRM Integration Patterns
Integrating AI agents with legacy ERP and CRM systems requires careful architecture. According to a 2025 survey by Accenture, 73% of enterprises struggle with legacy system integration when deploying AI agents.
# Integration pattern for legacy systems
class LegacySystemIntegration:
"""Pattern for integrating AI agents with legacy systems"""
def __init__(self):
self.adapters = {
'epic': EpicAdapter(),
'salesforce': SalesforceAdapter(),
'sap': SAPAdapter(),
'mainframe': MainframeAdapter()
}
self.orchestrator = IntegrationOrchestrator()
async def execute_agent_action(self, agent_action):
"""Execute agent action across multiple systems"""
# 1. Validate permissions
if not self._check_permissions(agent_action):
raise PermissionError("Insufficient permissions")
# 2. Transform request to system format
system_requests = self._transform_to_system_format(agent_action)
# 3. Execute in parallel where possible
results = await self.orchestrator.execute_parallel(system_requests)
# 4. Aggregate and normalize results
return self._aggregate_results(results)
3.2 Data Quality Prerequisites
AI agents need quality data. Enterprise data is often incomplete, inconsistent, or outdated. A 2025 Gartner study found that 68% of AI projects fail due to data quality issues.
Data Quality Framework:
- Completeness: Required fields present
- Accuracy: Data matches reality
- Consistency: Same data across systems
- Timeliness: Data is current
- Validity: Data conforms to schema
4. Missing Orchestration Layers
AI agents need orchestration. They make decisions, take actions, and need coordination. Most enterprise deployments lack proper orchestration layers.
4.1 Agent Orchestration Architecture
Orchestration layers coordinate agent actions, manage state, and handle failures. Major technology vendors have recognized this need and are providing enterprise-grade orchestration frameworks. Microsoft’s Agent 365, announced in November 2025, emphasizes the importance of orchestration for enterprise AI agents, while Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK) provides an open-source framework for building, testing, and deploying autonomous AI agents with built-in orchestration primitives.
Enterprise Orchestration Frameworks:
- Microsoft Agent 365: Integrated orchestration within Microsoft 365 ecosystem, designed to automate tasks and streamline workflows across digital environments
- Google Agent Development Kit (ADK): Open-source, model-agnostic framework with workflow orchestration primitives, supporting sequential, parallel, and loop constructs for coordinating multiple agents
Both frameworks address the critical infrastructure gap: providing the orchestration layer that enterprises need to deploy agentic AI at scale. Google ADK’s open-source approach offers flexibility and model-agnostic design, while Microsoft Agent 365 provides deep integration with existing Microsoft 365 workflows.
# Agent orchestration pattern
class AgentOrchestrator:
"""Orchestrates multiple AI agents in enterprise context"""
def __init__(self):
self.agents = {}
self.workflow_engine = WorkflowEngine()
self.state_manager = StateManager()
self.escalation_handler = EscalationHandler()
async def execute_workflow(self, workflow):
"""Execute multi-agent workflow"""
try:
# 1. Initialize workflow state
state = self.state_manager.create_state(workflow)
# 2. Execute steps sequentially or in parallel
for step in workflow.steps:
agent = self.agents[step.agent_type]
result = await agent.execute(step, state)
# 3. Update state
state = self.state_manager.update(state, result)
# 4. Check for escalation conditions
if self._needs_escalation(result):
await self.escalation_handler.handle(result)
return state
except Exception as e:
# Handle failures
await self._handle_failure(workflow, e)
raise
4.2 Monitoring and Observability
Enterprise AI agents need comprehensive monitoring. A SailPoint survey from December 2025 found that 96% of security professionals view AI agents as security threats due to limited visibility and control.
4.3 Escalation Paths
AI agents can’t handle everything. You need clear escalation paths:
- Low confidence: Escalate to human review
- High-risk actions: Require approval
- Errors: Fallback to human operator
- Edge cases: Route to specialized agents or humans
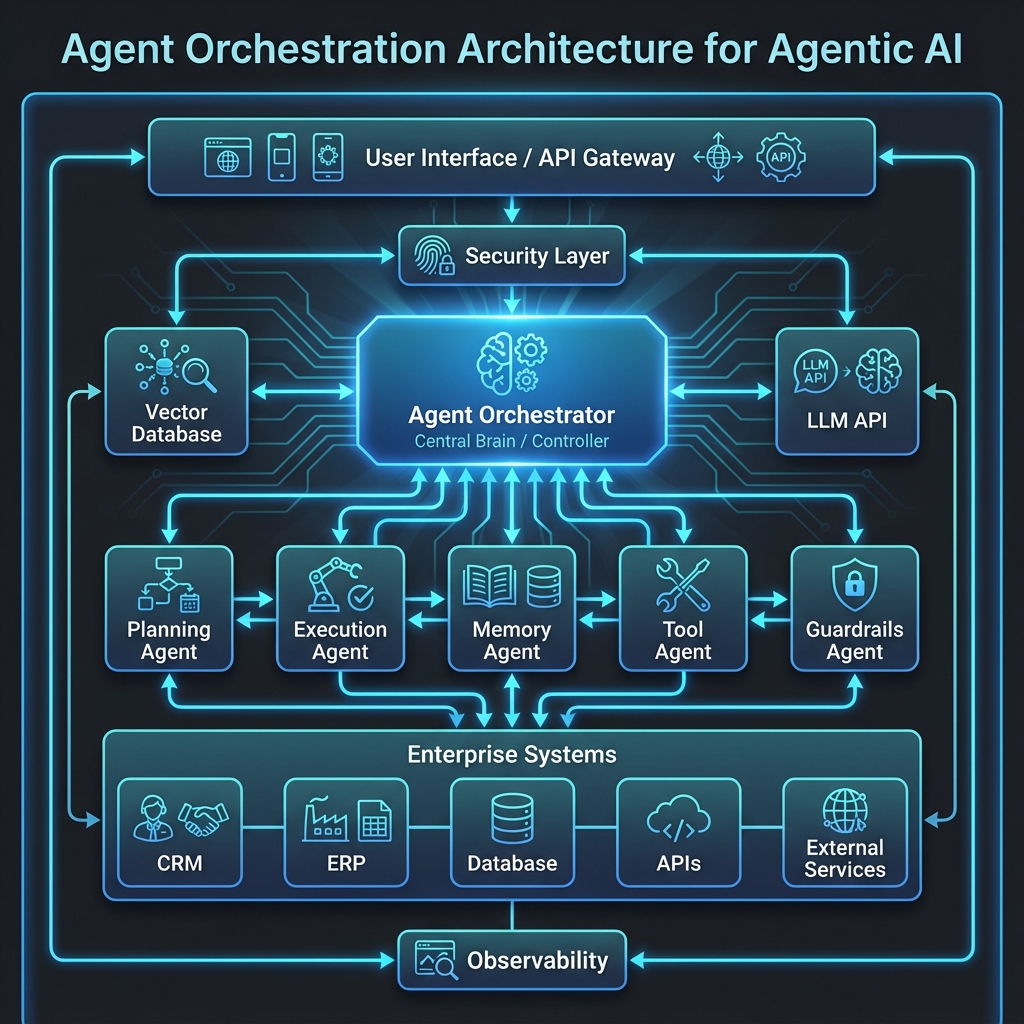
Figure 3: Agent Orchestration Architecture
5. Assessment Framework: Is Your Organization Ready?
5.1 Readiness Assessment Checklist
Use this framework to assess your organization’s readiness for agentic AI deployment:
| Category | Readiness Criteria | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Unified data access layer, API standardization, real-time data availability | 0-10 |
| Access Control | Fine-grained permissions, role-based access, audit logging | 0-10 |
| Observability | Agent monitoring, decision tracing, performance metrics | 0-10 |
| Orchestration | Workflow engine, state management, escalation paths | 0-10 |
| Governance | Compliance framework, data quality controls, risk management | 0-10 |
Scoring:
- 40-50: Ready for production deployment
- 30-39: Ready for pilot with gaps identified
- 20-29: Significant infrastructure work needed
- <20: Not ready—focus on infrastructure first
6. 6-12 Month Roadmap for Infrastructure Enablement
6.1 Months 1-3: Foundation
Data Integration Layer:
- Build unified data access APIs
- Standardize data formats across systems
- Implement data quality validation
- Create data catalog and lineage tracking
Access Control Framework:
- Implement fine-grained RBAC
- Build audit logging infrastructure
- Create permission management system
- Establish access review processes
6.2 Months 4-6: Orchestration
Workflow Engine:
- Deploy workflow orchestration platform
- Build state management system
- Implement escalation mechanisms
- Create workflow templates
Monitoring and Observability:
- Deploy agent monitoring platform
- Build decision tracing system
- Implement performance dashboards
- Create alerting and notification system
6.3 Months 7-9: Governance
Compliance Framework:
- Implement compliance controls
- Build audit trail system
- Create risk assessment framework
- Establish governance policies
6.4 Months 10-12: Pilot and Scale
Pilot Deployment:
- Deploy pilot agent in controlled environment
- Monitor and measure performance
- Iterate based on feedback
- Scale to production
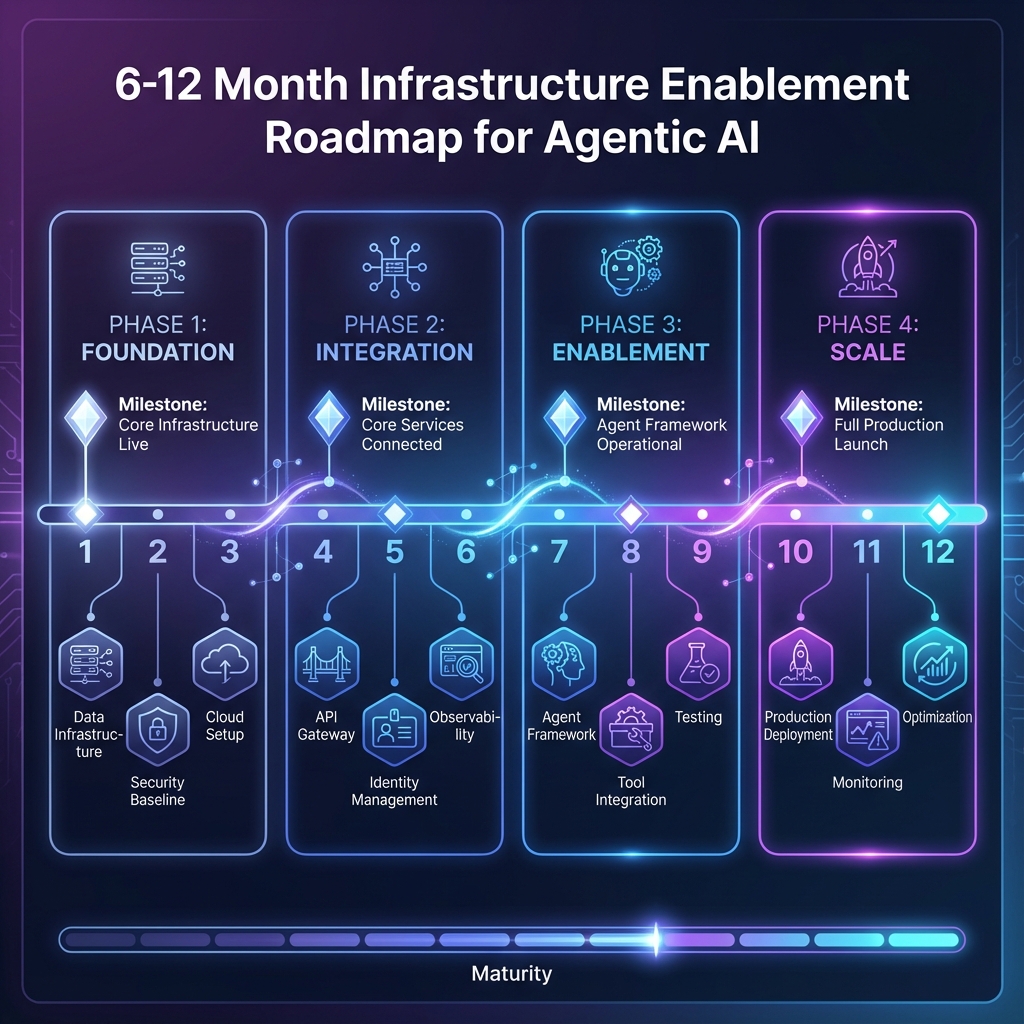
Figure 4: Infrastructure Enablement Roadmap
7. Healthcare Angle: Special Considerations for Regulated Environments
7.1 HIPAA Compliance Requirements
In healthcare, HIPAA compliance adds complexity. Every AI agent action must:
- Maintain audit trails: Log all PHI access
- Enforce access controls: Role-based permissions
- Encrypt data: In transit and at rest
- Support patient rights: Access, amendment, deletion
7.2 Audit Trail Requirements
Healthcare AI agents need comprehensive audit trails:
# HIPAA-compliant audit logging
class HIPAAAuditLogger:
"""Comprehensive audit logging for healthcare AI agents"""
def log_agent_action(self, agent, action, patient_id):
"""Log agent action with full HIPAA context"""
audit_entry = {
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat(),
'agent_id': agent.id,
'action': action.type,
'patient_id': patient_id, # PHI - encrypted
'reasoning': action.reasoning_chain,
'systems_accessed': action.systems_accessed,
'data_accessed': action.data_accessed, # PHI - encrypted
'user_id': action.initiated_by,
'compliance_flags': self._check_compliance(action)
}
# Store in tamper-proof audit log
self._store_audit_entry(audit_entry)
# Alert on compliance violations
if audit_entry['compliance_flags']:
self._alert_compliance_team(audit_entry)
7.3 GDPR Compliance for Healthcare in the EU and Ireland
For healthcare organizations operating in the EU and Ireland, GDPR compliance is mandatory. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) applies to all processing of personal data, including health data processed by AI agents.
Key GDPR Requirements for Healthcare AI Agents:
- Lawful basis for processing: Article 6 (lawful basis) and Article 9 (special categories including health data) require explicit consent or legal basis
- Data minimization: Process only necessary health data for the specific purpose
- Purpose limitation: Use health data only for stated purposes
- Storage limitation: Retain health data only as long as necessary
- Data subject rights: Right to access, rectification, erasure (“right to be forgotten”), data portability, and objection
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA): Required for high-risk processing, including AI systems processing health data
- Data Protection Officer (DPO): Mandatory for healthcare organizations processing health data
- Breach notification: Notify supervisory authority within 72 hours of a data breach
Ireland-Specific Considerations:
- Data Protection Commission (DPC): Ireland’s supervisory authority actively enforces GDPR
- Health Service Executive (HSE): Ireland’s public health service has specific data protection requirements
- National Health Information System: Integration with Ireland’s health information systems requires compliance
- Cross-border data transfers: Post-Brexit, transfers to UK require additional safeguards
# GDPR-compliant healthcare AI agent implementation
class GDPRCompliantHealthAgent:
"""GDPR-compliant AI agent for healthcare in EU/Ireland"""
def __init__(self):
self.dpo = DataProtectionOfficer()
self.consent_manager = ConsentManager()
self.audit_logger = GDPRAuditLogger()
async def process_health_data(self, patient_id, action):
"""Process health data with GDPR compliance"""
# 1. Verify lawful basis
if not self._has_lawful_basis(patient_id, action):
raise GDPRComplianceError("No lawful basis for processing")
# 2. Check consent (if required)
if action.requires_consent:
if not self.consent_manager.has_consent(patient_id, action.purpose):
raise ConsentRequiredError("Patient consent required")
# 3. Data minimization - only process necessary data
minimal_data = self._extract_minimal_data(patient_id, action)
# 4. Process with audit trail
result = await self._execute_action(minimal_data, action)
# 5. Log processing (GDPR Article 30 - records of processing)
self.audit_logger.log_processing({
'patient_id': patient_id, # Pseudonymized
'purpose': action.purpose,
'lawful_basis': action.lawful_basis,
'data_categories': action.data_categories,
'retention_period': action.retention_period,
'recipients': action.recipients,
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
return result
def handle_data_subject_request(self, patient_id, request_type):
"""Handle GDPR data subject rights requests"""
if request_type == 'access':
return self._provide_data_access(patient_id)
elif request_type == 'rectification':
return self._rectify_data(patient_id)
elif request_type == 'erasure':
return self._erase_data(patient_id) # Right to be forgotten
elif request_type == 'portability':
return self._export_data(patient_id) # Data portability
elif request_type == 'objection':
return self._stop_processing(patient_id)
7.4 EU AI Act Compliance for Healthcare
The EU AI Act, which became fully applicable in 2025, classifies healthcare AI systems as high-risk AI systems. This requires additional compliance measures beyond GDPR.
EU AI Act Requirements for Healthcare AI Agents:
- Risk management system: Continuous risk assessment and mitigation
- Data governance: Training, validation, and testing data quality management
- Technical documentation: Comprehensive documentation of AI system design and operation
- Record keeping: Maintain logs of AI system operations
- Transparency and information: Inform users that they are interacting with an AI system
- Human oversight: Human-in-the-loop for high-risk healthcare decisions
- Accuracy, robustness, and cybersecurity: Ensure AI system reliability and security
- Conformity assessment: Third-party assessment for certain high-risk systems
- CE marking: Required for high-risk AI systems placed on the EU market
Healthcare-Specific AI Act Requirements:
- Medical device classification: If AI system is a medical device, comply with EU MDR (Medical Device Regulation)
- Clinical evaluation: Demonstrate safety and performance through clinical evidence
- Post-market surveillance: Monitor AI system performance and adverse events
- Notified body assessment: For Class IIb and Class III medical devices
# EU AI Act compliant healthcare AI agent
class EUAIActCompliantHealthAgent:
"""EU AI Act compliant healthcare AI agent"""
def __init__(self):
self.risk_manager = RiskManagementSystem()
self.data_governance = DataGovernanceFramework()
self.technical_docs = TechnicalDocumentation()
self.human_oversight = HumanOversightManager()
async def make_clinical_decision(self, patient_data, clinical_context):
"""Make clinical decision with EU AI Act compliance"""
# 1. Risk assessment
risk_level = self.risk_manager.assess_risk(patient_data, clinical_context)
# 2. Transparency - inform user
self._inform_user_ai_interaction()
# 3. Human oversight for high-risk decisions
if risk_level == 'high':
decision = await self.human_oversight.review_decision(
patient_data,
clinical_context
)
else:
decision = await self._ai_decision(patient_data, clinical_context)
# 4. Record keeping
self.technical_docs.log_operation({
'decision': decision,
'risk_level': risk_level,
'data_used': patient_data,
'human_review': risk_level == 'high',
'timestamp': datetime.now().isoformat()
})
# 5. Post-market surveillance
self._monitor_performance(decision, patient_data)
return decision
def _inform_user_ai_interaction(self):
"""EU AI Act Article 13 - transparency requirement"""
# Display notice that user is interacting with AI system
pass
Ireland-Specific EU AI Act Implementation:
- National AI Office: Ireland’s coordination body for AI Act implementation
- Market Surveillance Authority: Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) for medical devices
- Conformity assessment bodies: Irish notified bodies for medical device certification
- Reporting requirements: Report serious incidents to HPRA and EU database
Combined GDPR + EU AI Act Compliance Framework:
Healthcare organizations in Ireland and the EU must comply with both GDPR and EU AI Act. This requires:
- Integrated compliance program: Unified approach to both regulations
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) + AI Act conformity assessment: Combined risk assessment
- Unified audit trails: Logs that satisfy both GDPR (Article 30) and AI Act (Article 12) requirements
- Dual documentation: Technical documentation for AI Act and processing records for GDPR
- Coordinated breach response: Notify both DPC (GDPR) and market surveillance authority (AI Act)
7.5 Healthcare-Specific Governance
Healthcare organizations need additional governance beyond regulatory compliance:
- Clinical decision support: Validation of AI recommendations
- Provider oversight: Physician review of AI actions
- Patient safety: Safety monitoring and reporting
- Regulatory reporting: Compliance with FDA (US), HPRA (Ireland), EMA (EU) requirements
- Ethical AI framework: Ensure AI decisions align with medical ethics
- Bias mitigation: Ensure AI systems don’t discriminate against patient groups
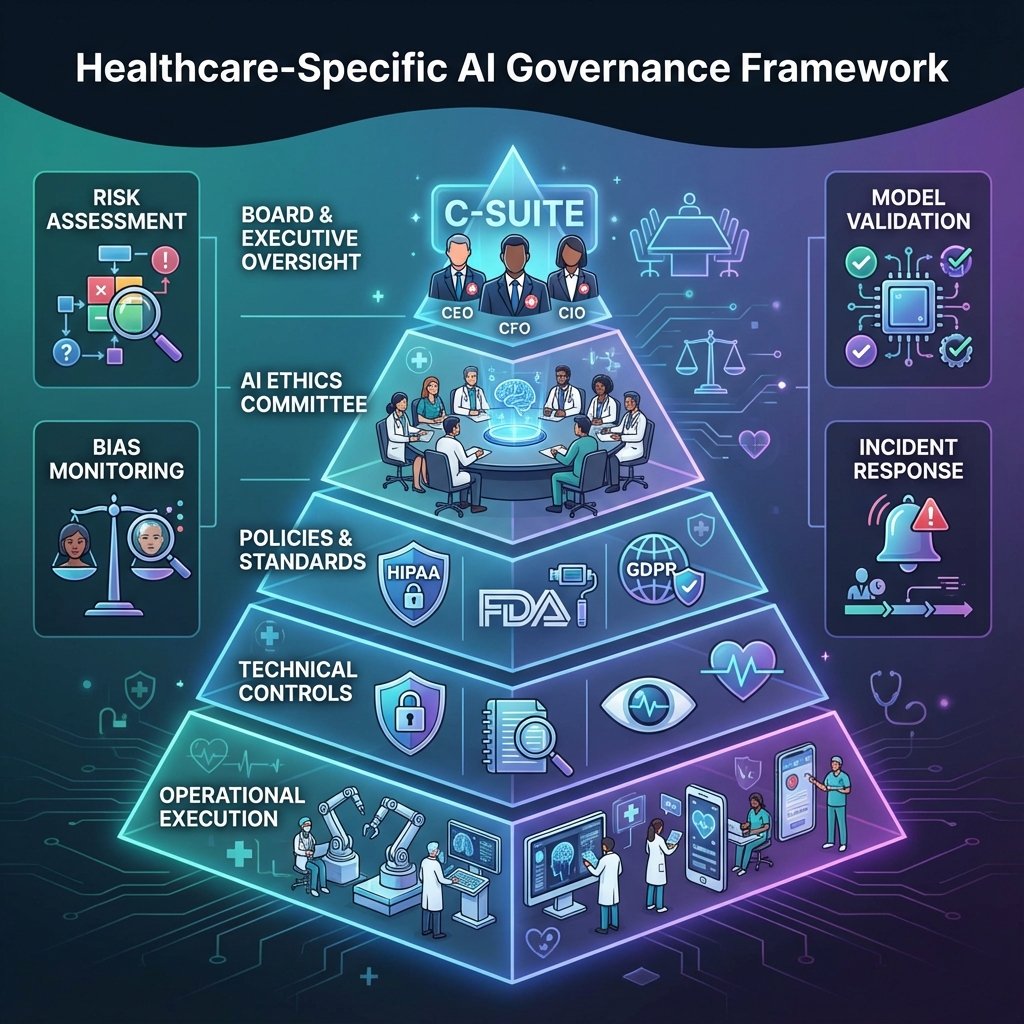
Figure 5: Healthcare AI Governance Framework
8. Best Practices: Lessons from Enterprise Deployments
Based on real enterprise deployments, here are the practices that work:
- Start with infrastructure: Don’t deploy agents until infrastructure is ready
- Build integration layers: Abstract legacy systems behind modern APIs
- Implement governance early: Establish policies before deployment
- Monitor everything: Comprehensive observability is essential
- Plan for escalation: Always have human oversight
- Test thoroughly: Test in production-like environments
- Iterate based on feedback: Continuous improvement is key
9. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Based on failed deployments, avoid these mistakes:
- Deploying before infrastructure is ready: Leads to project cancellation
- Ignoring legacy systems: Integration is harder than you think
- Underestimating governance: Compliance is non-negotiable
- Lack of observability: You can’t manage what you can’t see
- No escalation paths: Agents will encounter edge cases
- Poor data quality: Garbage in, garbage out
- Inadequate access controls: Security risks are real
10. Conclusion: Infrastructure First, Then AI
The hard truth: infrastructure readiness matters more than model capability. Gartner’s prediction that 40% of agentic AI projects will be cancelled isn’t about AI—it’s about infrastructure.
Before deploying agentic AI, ensure your organization has:
- Unified data access and integration
- Fine-grained access controls and audit trails
- Comprehensive observability and monitoring
- Orchestration and workflow management
- Governance and compliance frameworks
In healthcare, add HIPAA compliance, clinical oversight, and patient safety monitoring. These aren’t optional—they’re essential.
The roadmap is clear: 6-12 months of infrastructure enablement, then pilot deployment, then scale. Skip the infrastructure work, and you’ll join the 40% of cancelled projects.
The models are ready. The question is: Is your infrastructure?
References
- Gartner. (2025, August 26). “Gartner Predicts 40 Percent of Enterprise Apps Will Feature Task-Specific AI Agents by 2026, Up from Less Than 5 Percent in 2025.” Gartner Newsroom. Retrieved from gartner.com
- Gartner. (2025, October 7). “Gartner Says Agentic AI Supply Exceeds Demand, Market Correction Looms.” Gartner Newsroom. Retrieved from gartner.com
- Anthropic. (2025, December 22). “Anthropic Takes the Fight to OpenAI with Enterprise AI Tools – And They’re Going Open Source Too.” TechRadar. Retrieved from techradar.com
- Microsoft. (2025, November 18). “Microsoft Doubles Down on Agentic AI – Agent 365 Prepares for a Future with Over 1 Billion Agents.” Windows Central. Retrieved from windowscentral.com
- Google. (2025). “Google Agent Development Kit (ADK) – Open-Source Framework for Building Autonomous AI Agents.” Google Cloud. Retrieved from github.com/google/adk-docs
- GeeksforGeeks. (2025). “What is Google ADK (Agent Development Kit)? – A Comprehensive Guide.” GeeksforGeeks. Retrieved from geeksforgeeks.org
- InfoQ. (2025, November). “Google Releases Agent Development Kit for Go – Enabling Multi-Agent Systems.” InfoQ. Retrieved from infoq.com
- Snowflake. (2025, December 5). “Snowflake Inks $200M Deal with Anthropic to Drive ‘Agentic AI’ in the Enterprise.” IT Pro. Retrieved from itpro.com
- SailPoint. (2025, December). “Love and Hate: Tech Pros Overwhelmingly Like AI Agents But View Them as a Growing Security Risk.” TechRadar. Retrieved from techradar.com
- Accenture. (2025). “Accenture Helps Organizations Advance Agentic AI with Gemini Enterprise.” Accenture Newsroom. Retrieved from newsroom.accenture.com
- Amazon Web Services. (2025, October 10). “Amazon Quick Suite Wants to Help Your Business Build Its AI Agents in No Time at All.” TechRadar. Retrieved from techradar.com
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.