After two decades of building language-aware systems, I have witnessed the most profound transformation in how machines understand and generate human language. The emergence of generative AI has fundamentally altered the NLP landscape, moving us from rigid rule-based systems to fluid, context-aware models that can engage in nuanced dialogue, create compelling content, and reason about complex linguistic structures. This evolution represents not just a technological shift but a paradigm change in human-computer interaction.
The Foundation: Understanding Modern NLP Architecture
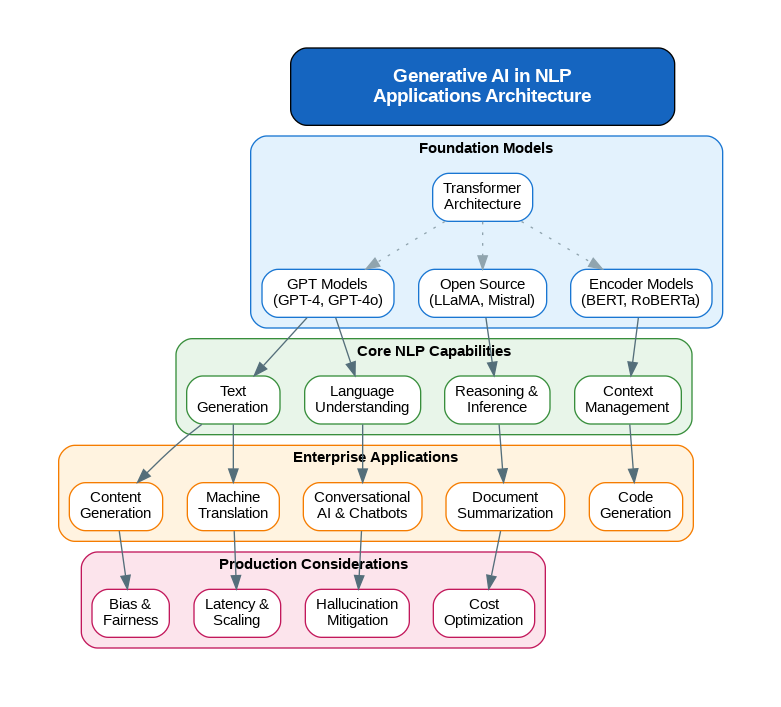
The transformer architecture, introduced in the seminal “Attention is All You Need” paper, revolutionized how we approach language understanding. Unlike earlier recurrent neural networks that processed text sequentially, transformers use self-attention mechanisms to consider all words in a sentence simultaneously, capturing long-range dependencies that were previously difficult to model. This architectural innovation enabled the development of increasingly powerful language models.
GPT-4 and its successors represent the current state of the art, demonstrating emergent capabilities that surprised even their creators. These models can perform complex reasoning, follow nuanced instructions, and generate text that is often indistinguishable from human writing. The progression from GPT-3’s 175 billion parameters to more efficient architectures shows that raw scale is being complemented by architectural innovations and training methodology improvements.
Beyond Chatbots: The Expanding Application Landscape
While conversational AI captures headlines, the applications of generative NLP extend far beyond chatbots. In my production deployments, I have implemented systems for automated document summarization that reduce legal review time by 60%, code generation assistants that accelerate developer productivity, and content localization pipelines that maintain brand voice across 40+ languages. Each application requires careful consideration of the specific NLP capabilities needed and the production constraints involved.
Machine translation has evolved from phrase-based statistical methods to neural approaches that understand context and idiom. Modern translation systems can preserve tone, handle domain-specific terminology, and even adapt formality levels based on the target audience. The quality improvements have made real-time translation viable for business-critical communications.
Production Considerations: Hallucination and Reliability
The most significant challenge in deploying generative AI for NLP applications is managing hallucination, where models generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. In enterprise deployments, I implement multiple mitigation strategies including retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to ground responses in verified data sources, confidence scoring to flag uncertain outputs, and human-in-the-loop workflows for high-stakes decisions.
Latency and cost optimization become critical at scale. Techniques like model distillation, quantization, and intelligent caching can reduce inference costs by 80% while maintaining acceptable quality. The choice between cloud-hosted APIs and self-hosted models depends on data sensitivity, volume, and latency requirements specific to each use case.
Ethical Dimensions and Responsible Deployment
Bias in language models reflects and can amplify biases present in training data. Responsible deployment requires systematic bias auditing, diverse evaluation datasets, and ongoing monitoring of model outputs. The potential for misuse in generating misinformation or manipulative content demands robust content policies and technical safeguards.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what generative AI can accomplish in NLP, the focus must remain on building systems that augment human capabilities while maintaining transparency, accountability, and ethical standards. The technology is powerful, but its value ultimately depends on how thoughtfully we deploy it.
Discover more from C4: Container, Code, Cloud & Context
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.